Lab - 7: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol¶
Objectives¶
The lab is on observations of:
Dynamic configuration of a host with an IP address assignment
Broadcast domains and DHCP servers
DHCP lease information on IP addresses that are in use
Load Lab Network¶
Execute the commands to load the labpicker:
%load_ext uhed
%lab
In order to conduct this lab, please pick DHCP lab from the dropdown menu and click on the Build Network button. Once successfully built, display the network topology using:
NET.showTopo()
Open a terminal using the File, New, Terminal from top menu and then
ssh (secure shell) into the hosts using the command:
gssh <username> <devicename>
Reminder Example on ssh
For example, for a user name, student01, ssh
into the host1 using the command gssh student01 host1 at the terminal.
Topology Orientation¶
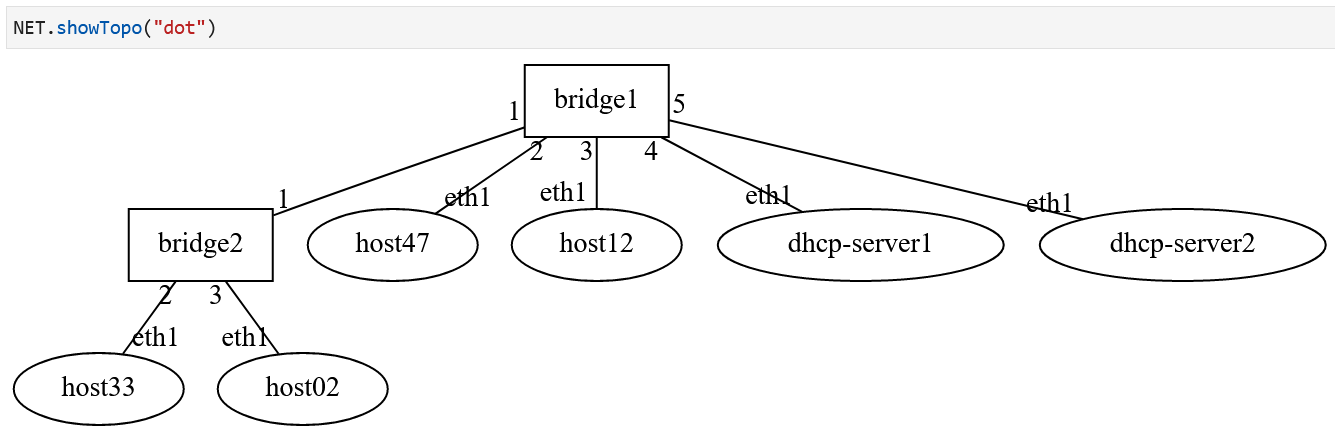
Lab Network Topology: There are two DHCP servers and 4 hosts. Both DHCP servers are
on the same bridge, bridge1.¶
Observation Guideline¶
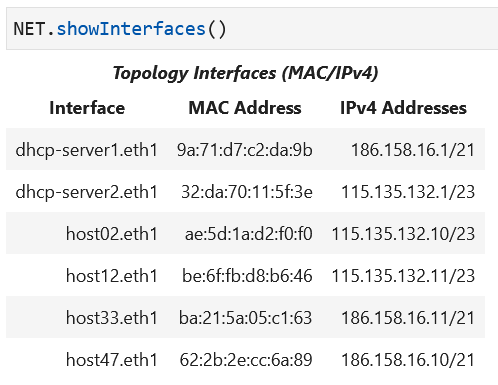
Determine the initial state of the network that has been built, including IP and MAC addresses of the hosts:
NET.showInterfaces()
On the iPython lab notebook, execute
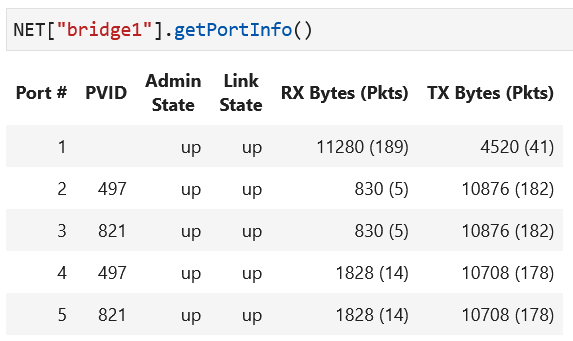
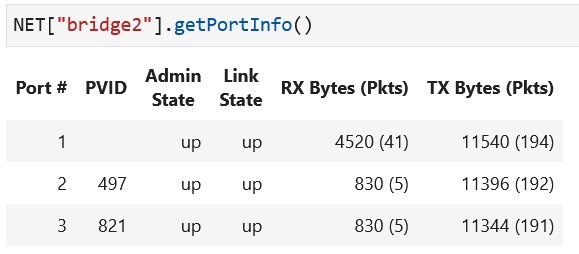
NET["bridge1"].getPortInfo()andNET["bridge2"].getPortInfo()to retrieve the current VLAN configuration of ports.Again on the lab notebook, execute
NET["dhcp-server1"].getLeaseInfo()andNET["dhcp-server2"].getLeaseInfo()to see what IP addresses are leased out in the network. Initially, DHCP servers would have no IP addresses in their lease information tables.On one host in each VLAN domain, start
tcpdumpto monitor the packets sent in the next step. Use the following command to filter out unwanted packets in the output:# tcpdump -i eth1 -ne not ether dst 01:80:c2:00:00:00 and not ether proto 0x86DDAt the terminals for the hosts, issue the command
dhclient -v eth1to enable the DHCP client application to start inverbosemode as indicated with the argument-vand on the interfaceeth1.Back on the lab notebook, execute
NET["dhcp-server1"].getLeaseInfo()andNET["dhcp-server2"].getLeaseInfo()to see what IP addresses are leased out now. Verify these IP addresses show up on the hosts using the notebook command (NET.showInterfaces()).
The output for lease information tables will indicate the lease time and the IP address assignment to the hosts.
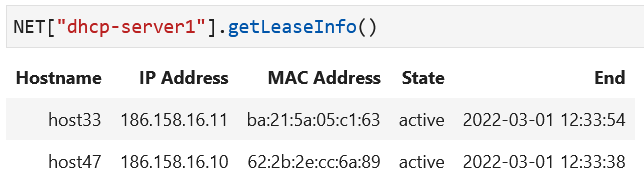
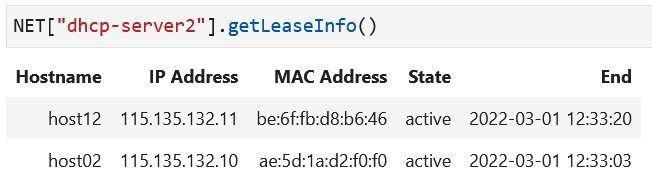
Sample output after all hosts have run dhclient to retrieve their
host configuration from the DHCP servers.¶
Starting DHCP Client at a Host¶
The DHCP server interfaces should have IP addresses configured. The host interface table should look like the following:
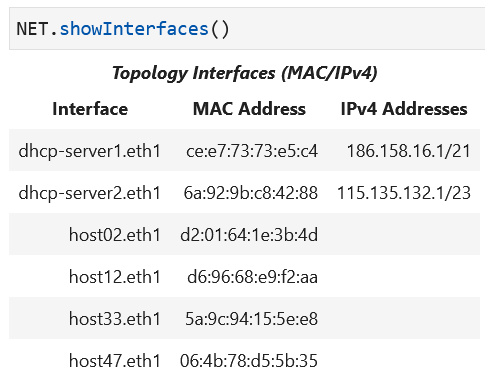
At the onset of this lab,
the hosts should not be configured with IP addresses
on the eth1 interfaces.
Now, check the host route table, which should be empty:
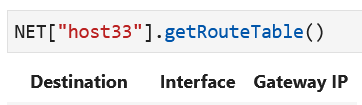
The command dhclient -v eth1 executed on a host terminal will cause the host to request a dynamically
assigned IP address for the subnet being served by the DHCP server. Below is an example of the output of
a successful DHCP IP address assignment, as displayed on the host terminal.
dgurkan@cot-cn:~$ gssh dgurkan host33
/ # dhclient -v eth1
Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client 4.4.2-P1
Copyright 2004-2021 Internet Systems Consortium.
All rights reserved.
For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/
Listening on LPF/eth1/da:55:4c:84:ee:d7
Sending on LPF/eth1/da:55:4c:84:ee:d7
Sending on Socket/fallback
DHCPDISCOVER on eth1 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 7
DHCPDISCOVER on eth1 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 12
DHCPDISCOVER on eth1 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 17
DHCPDISCOVER on eth1 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 7
DHCPOFFER of 186.158.16.10 from 186.158.16.1
DHCPREQUEST for 186.158.16.10 on eth1 to 255.255.255.255 port 67
DHCPACK of 186.158.16.10 from 186.158.16.1
bound to 186.158.16.10 -- renewal in 437 seconds.
/ #
Once dhclient has been executed on all hosts, the host interfaces should all be configured with IP addresses.
Verify this updated state.
Host interface information can also be pulled for each individual host using the command following command in the notebook:
NET[<host-label>].getInterfaceInfo()
Lastly, now that the host has an assigned IP address on eth1, the host route table should have at least one
entry, the route to this host’s subnet on eth1. Below is an example route table as displayed in the notebook:
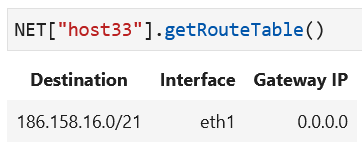
Attention
The bridges in this lab have port VLAN configurations. Please examine port VLANs to identify the broadcast domains in the topology.
Learning Activities¶
Step 1
Start tcpdump running on two hosts as mentioned in the observation plan.
Step 2
Run the command dhclient -v eth1 on every host in your network so that they are
assigned an IP address. Observe the tcpdump output after running dhclient on
each host. Which hosts receive packets and what packet types are received by the
various hosts in the network?
Step 3
Issue a ping on the command line to a destination IP address
(documentation is available on the ping tool) for each
host within their own subnet and also outside of their subnet to observe the results.
Step 4
Investigate the ARP tables at hosts by issuing this command in the lab notebook:
NET[<host-label>].getARPTable()
Step 5 – Homework
5a. Ensure all hosts have retrieved IP addresses from their respective DHCP servers by checking all host interfaces have IP addresses and leases for each host interface exist in the DHCP server lease table.
5b. In your lab notebook, complete the submission of your assignment:
There are two steps to complete your assignment:
1. In your lab notebook, run:
%homeworkto complete and submit this portion.
2. In your notebook, run:
%exerciseto solve the question(s) and submit this portion.
Caution
You only have one submission attempt available to you. It is recommended to complete the lab requirements before you load the homework to prevent submitting incomplete data.
Lab Wrap-up
Please follow the instructions to delete your reserved topology and then close and halt your lab notebook and any open terminals on the lab service.